No products added!
When the skin is exposed to too much heat, a burn occurs. It is also said that “too much heat in the skin” always leads to a burn or burn. This can be a first, second or third degree burn.
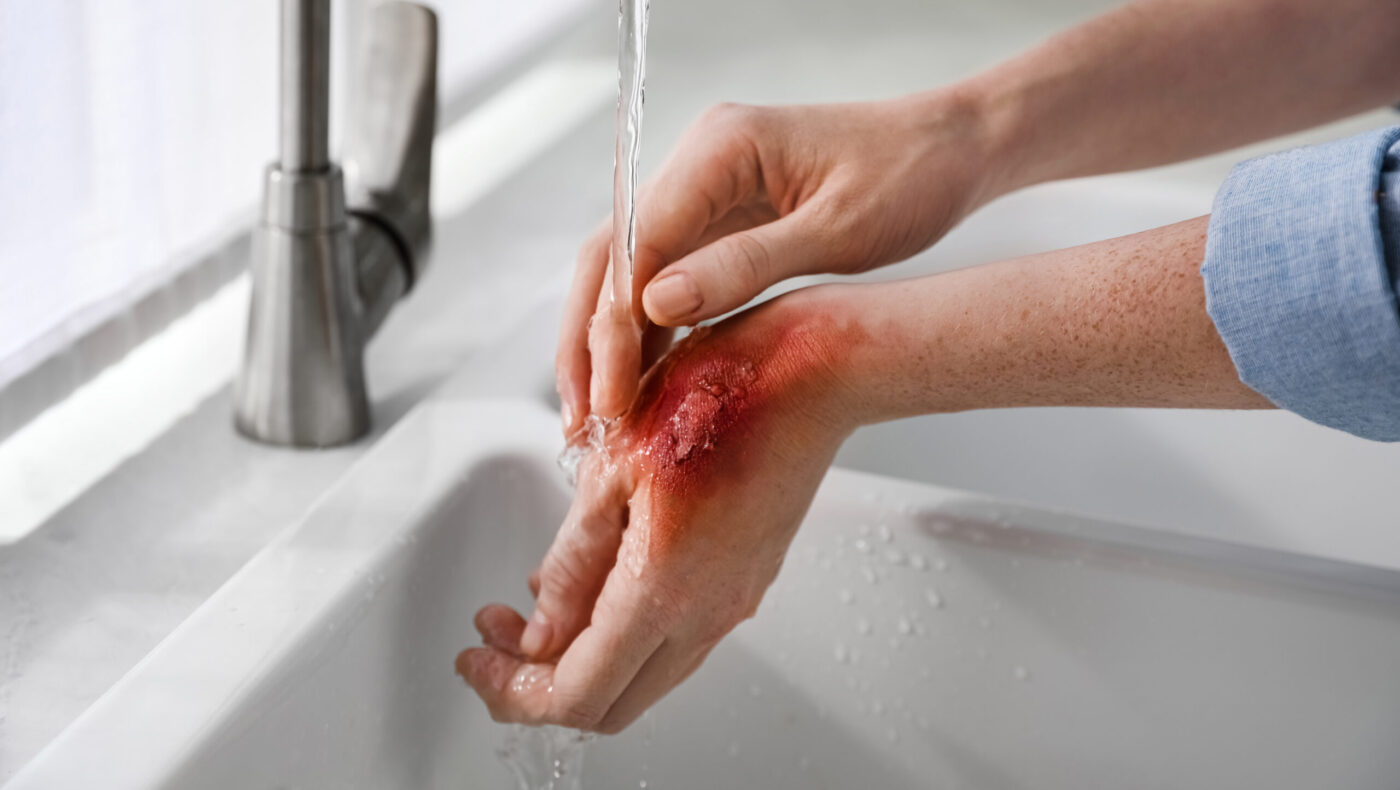

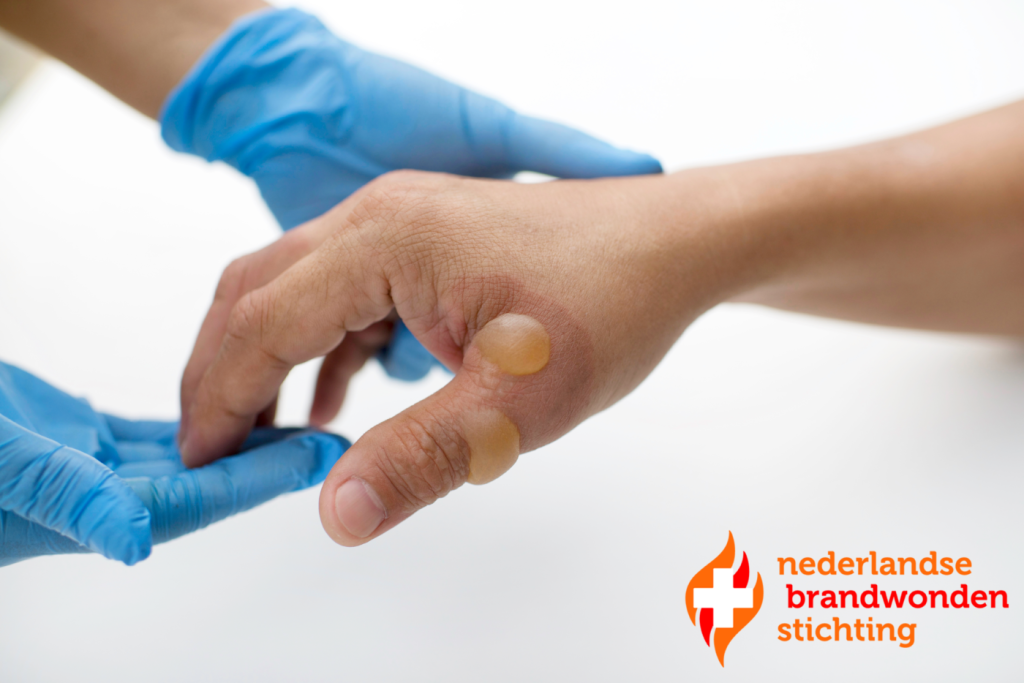
First-degree burns are the least serious form of heat damage and recover after a few days. We only call this burn a burn if the skin is broken. When there is only overheating, we call this a burn of the skin. A good example of a house burn is sitting in the sun for too long. The skin will turn red, but will not blister. The epidermis is pink to red and feels dry. The burn is painful and sometimes somewhat swollen.
Third-degree burns are the most serious. With this type of burn, both the epidermis and dermis, down to the underlying fatty tissue, will be completely burned and damaged. The wound may look black, brown, beige, or white, depending on what type of heat source burned the skin. The wound will not feel painful because the nerve endings are damaged. However, the edges of the burn will feel red and painful because the nerve tissue here still functions well and these are second-degree burns.

Staudt® wound ointment helps accelerate the natural wound healing process by forming a protective layer on the wound bed. This protects the wound against irritants, viruses, bacteria, fungi and yeasts and promotes wound recovery by preventing moisture loss. The benefits for you as a patient are disinfection of the wound, care and protection of the wound, support for wound recovery, reduction of irritation and pain around the wound and reduction of scar formation.
If the skin is burned and no wound has occurred, we recommend that you give the skin rest to recover after cooling it with water. We then recommend that you use Staudt® Scar Cream. Our cream effectively hydrates the skin, prevents moisture loss and supports skin recovery after burns and burns without causing irritation or further drying out the skin.
Chemical burns are caused by the skin (layers) coming into contact with chemicals. Thermal burns occur when the skin comes into contact with heat. The initial reaction to a chemical burn is similar to a thermal burn: blisters and burns may occur.
In the case of a chemical burn, damage to the skin (barrier) may allow the chemical to easily enter the bloodstream. Each chemical is different from the other and requires a different approach. However, rinsing with water is the first step. By rinsing you dilute the concentration of the substance and the aggressiveness will decrease. If the fabric comes into contact with your skin through clothing, remove it immediately.
If you come into contact with a (heavy) chemical substance, always call your doctor immediately or call 112.
A thermal or chemical burn almost always leads to a scar, the severity depends on the nature, location and depth of the injury. So how serious and extensive the subsequent scar will be depends largely on how large and deep the burn was. The body always wants to recover as quickly as possible and therefore creates new (scar) tissue at the site of the damage during the healing process. Logically, a first-degree burn – where the skin remains intact – will show better recovery than a third-degree burn where the deeper layers of the skin (down to the underlying fatty tissue) are burned. The wounds here are deep and will cause a greater variation in the severity of the complaints and the type of scar. During the healing process, the body repairs the skin at the site of damage or burns by creating scar or repair tissue. The skin here is not able to grow completely new. Because the damage is sometimes deep and extensive, excessive scar tissue can develop.
Our cream – developed by plastic surgeons – helps keep the scar tissue, which can sometimes feel painful or hard, supple and soft.
Staudt® Scar Cream effectively hydrates the skin, prevents moisture loss and supports the skin’s recovery after burns and burns without causing irritation or further drying out the skin.
The benefits of our cream for you as a patient are:
The Staudt® brand guarantees effective solutions and expert help in the care of damaged skin. Years of use in the Red Cross hospital and the Beverwijk Burn Center have proven that our creams are effective and score high on satisfaction among our users – more than 90% of people are happy with our product!
Staudt Medical Skin Care works closely with the Burn Foundation, contributes to research and sponsors burn patients with our scar products as long as the need exists.